New Sea Cucumber Species Joins the Research Toolbox

Contact: Diana Kenney
dkenney@mbl.edu; 508-685-3525
WOODS HOLE, Mass. -- Scientists have a handful of standard research organisms, including fruit flies and mice, that they use to study the evolutionary development (evo-devo) of animal lineages over time. Yet the more research organisms they can study, the deeper our understanding of life and the more knowledge we have to advance biomedicine and ecological conservation.
Researchers at the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), Woods Hole, and the Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn (SZS) in Naples, Italy, have added to the evo-devo toolbox by establishing Holothuria tubulosa, a species of sea cucumber, as an experimental research organism. They published their protocols recently in Frontiers in Evolutionary Developmental Biology.
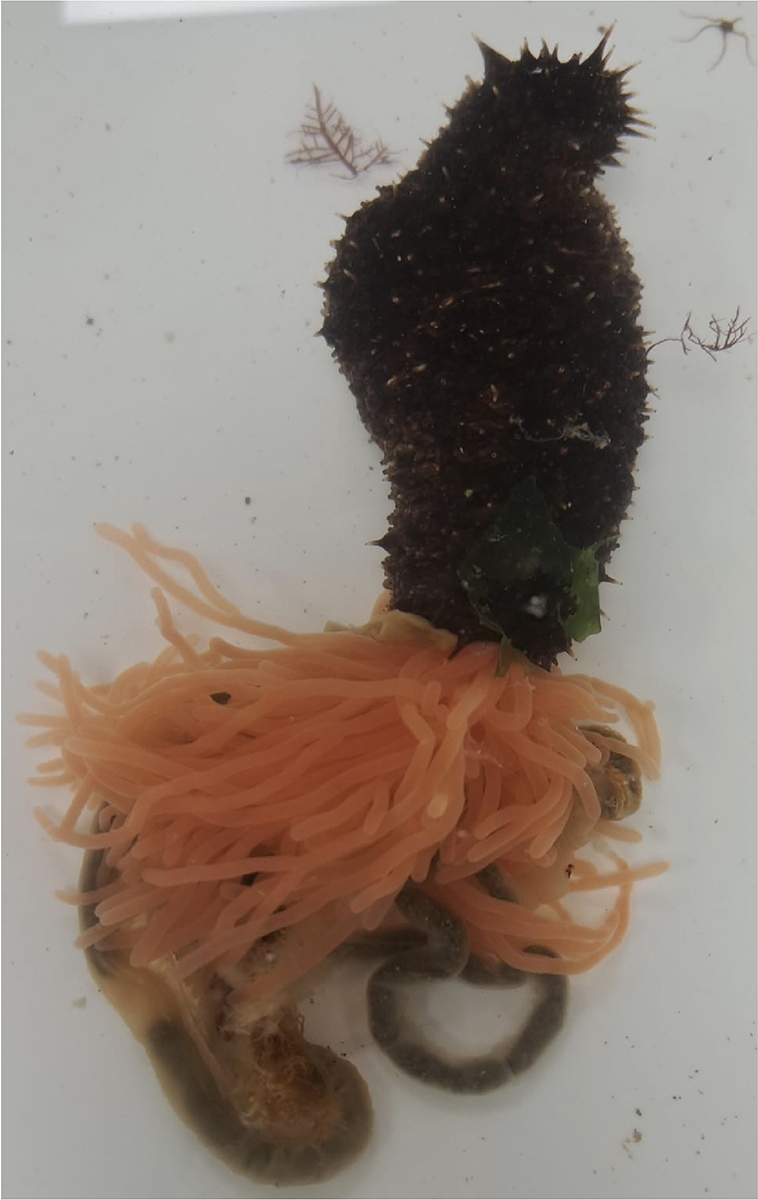
The sea cucumber, found abundantly in the Mediterranean Sea and the eastern Atlantic Ocean, is an echinoderm, a group of marine invertebrates that includes sea urchins, sea stars and sand dollars. Some species of echinoderms have been used as developmental models for over a century thanks to their low costs, high fecundity, optically clear larvae and, more recently, amenability to genetic studies.
“Echinoderms are the closest invertebrates to humans genetically, which means we have most of our genes in common. If we understand how those genes function in an echinoderm, than we also know how they function in humans,” said Margherita Perillo, a research scientist at MBL who led the study.
“Sea cucumbers also have attributes and special skills — such as being deposit feeders, which cleans the ocean floor, and the ability to completely regenerate their whole body — that could be useful in conservation and biomedicine,” she said.
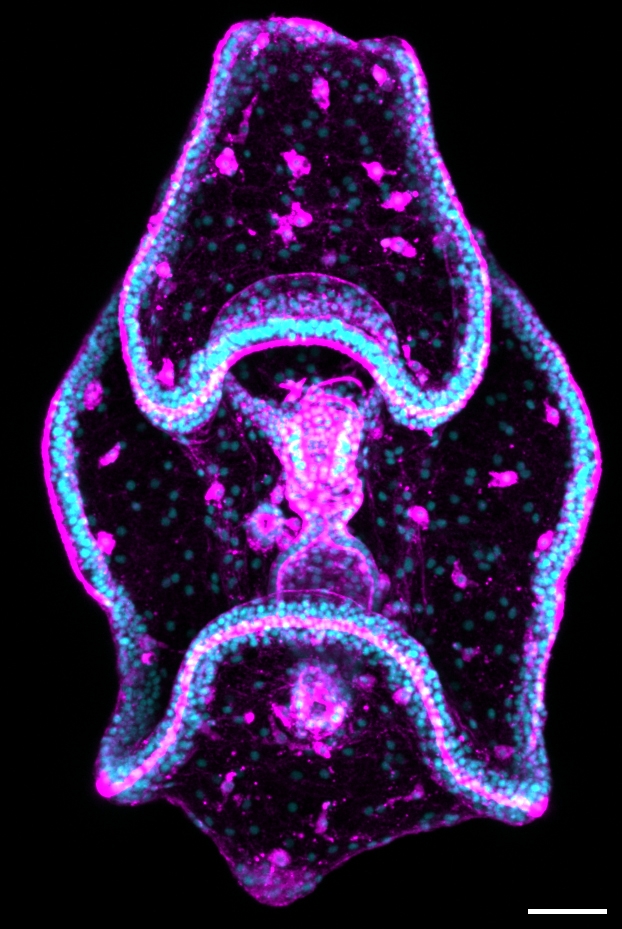
Protocol for producing embryonic cultures
The first step in establishing H. tubulosa as a research organism was to develop a protocol to efficiently produce embryonic cultures in a lab setting. Existing methods, including mimicking the animal’s natural breeding cycle and inducing the release of all the animal’s organs by evisceration (a behavior that sea cucumbers normally exhibit when threatened) were complicated, inefficient or both.
To overcome this, the team led by Rossella Annunziata (SZS) and Perillo pioneered a noninvasive technique to repeatedly harvest a small number of gametes (sperm and eggs) over a long period of time. The microsurgery involves a small incision near a sea cucumber’s reproductive organs, allowing for the retrieval of testes or ovaries. The incision heals quickly and gives researchers the ability to harvest every few days from the same animal.
Since eggs retrieved using this technique have not reached maturation and cannot be fertilized, the researchers next expose the harvested ovaries to a synthetic peptide – Thioredoxin-2 peptide, known to work in another species – to make them receptive to sperm. They then grow the fertilized egg in a culture, where it reaches the metamorphosis stage in about eight weeks.
“Our protocol removes a major bottleneck that has kept H. tubulosa from being used as a research organism and opens the door for more scientists to use it,” Perillo said.

Building on a strong foundation
The team next used high-resolution microscopy coupled with immunohistochemistry to document the development of the larvae, with a focus on its unique structures. Their detailed description will serve as a foundation for future studies that aim to use genetic manipulations to functionally dissect development in H. tubulosa.
Additionally, they provided an example of how scientists can use echinoderm larvae to study the diversification of anatomical structures in closely related organisms. In this case, they used serotonin immunostaining to show how the location of serotonin neurons differed between types of echinoderms. Why and how this diversification occurs is an open question in evolutionary development biology.
Perillo received an Emerging Research Organisms grants from the Society of Developmental Biology to support her work and to continue her study of H. tubulosa.
“The sea cucumber is a fascinating animal and the better we understand it, the more value it has as a research organism,” said Perillo. “My plan now is to develop genetic tools to help further characterize it as an emerging comparison model in evo-devo. At the same time, this collaborative work laid the foundation to establish a new sea cucumber species here at the MBL”
Citation:
Perillo, Margherita et al. (2024) Larval development of Holothuria tubulosa, a new tractable system for evo-devo. Front. Ecol. Evol., DOI: 10.3389/fevo.2024.1409174.
—###—
The Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) is dedicated to scientific discovery – exploring fundamental biology, understanding marine biodiversity and the environment, and informing the human condition through research and education. Founded in Woods Hole, Massachusetts in 1888, the MBL is a private, nonprofit institution and an affiliate of the University of Chicago.